What drives electrification?
There was time when all systems aboard an aircraft were mechanical. Over time, smaller batteries made their way into onboard systems in the flight deck. Eventually the maturation of batteries for propulsions systems (as experienced in the automotive industry) provided sufficient power to replace conventional propulsion technologies in aircraft. Electric propulsion is more than just battery technologies – it chartered a course for overall electrification and triggered a design revolution, for both airframe and propulsion system.
Benefits go beyond market interest in electric aircraft – electrification mirrors the greater environmental consciousness of European citizens, answers the European demand for sustainable and smart air transport and mobility, while promising more economic operations.

What technology is involved?
Electrification of propulsion can mean:

Fully electric propulsion, using batteries or hydrogen fuel cells and motor(s)
Hybrid-electric propulsion, using a conventional engine, fuel, and a generator distributing electric power
This complements the electrification of onboard hydraulic and pneumatic systems, such as slats, flaps, stabilizers, environmental control systems, de-icing, and more.
What are the advantages to electric & hybrid-electric propulsion?
From an engineering and manufacturing perspective:
- More flexibility in design
- Less parts and components
- Simplified production
From an operational perspective:
- Lighter maintenance and improved monitoring
- Reduced operational costs – by approx. 30%
- Increased safety thanks to systems redundancy

From a general public perspective:
- No negative contribution to climate change when running on sustainable power
- Improved connectivity and mobility options
- Increased and more affordable access to careers in aviation
From an environmental perspective:
- Sustainable power obtainable from renewable sources
- Low to zero particulate emissions in flight
- Lower operative noise, opening previously inaccessible airspace
What are the challenges of electric propulsion?
Battery/fuel-cell weight and power density initially offer low range
Availability of batteries and charging infrastructure
The end-of-life solution for batteries is an industry of its own
What about the certification of these technologies?
EASA provides manufacturers the opportunity to certify this technology, either as an engine or part of the type certification of an aircraft.For more information, please visit their webpage.
Which European manufacturers are developing electric aircraft or propulsion today?






GALLERY
Three biggest milestones in the type-certification of aircraft engines
29 March 1927
First Type Certified Aircraft with a Piston Engine
Buhl-Verville CA-3


2 May 1952
First Type Certified Commercial Aircraft with a Jet Engine
De Havilland Comet
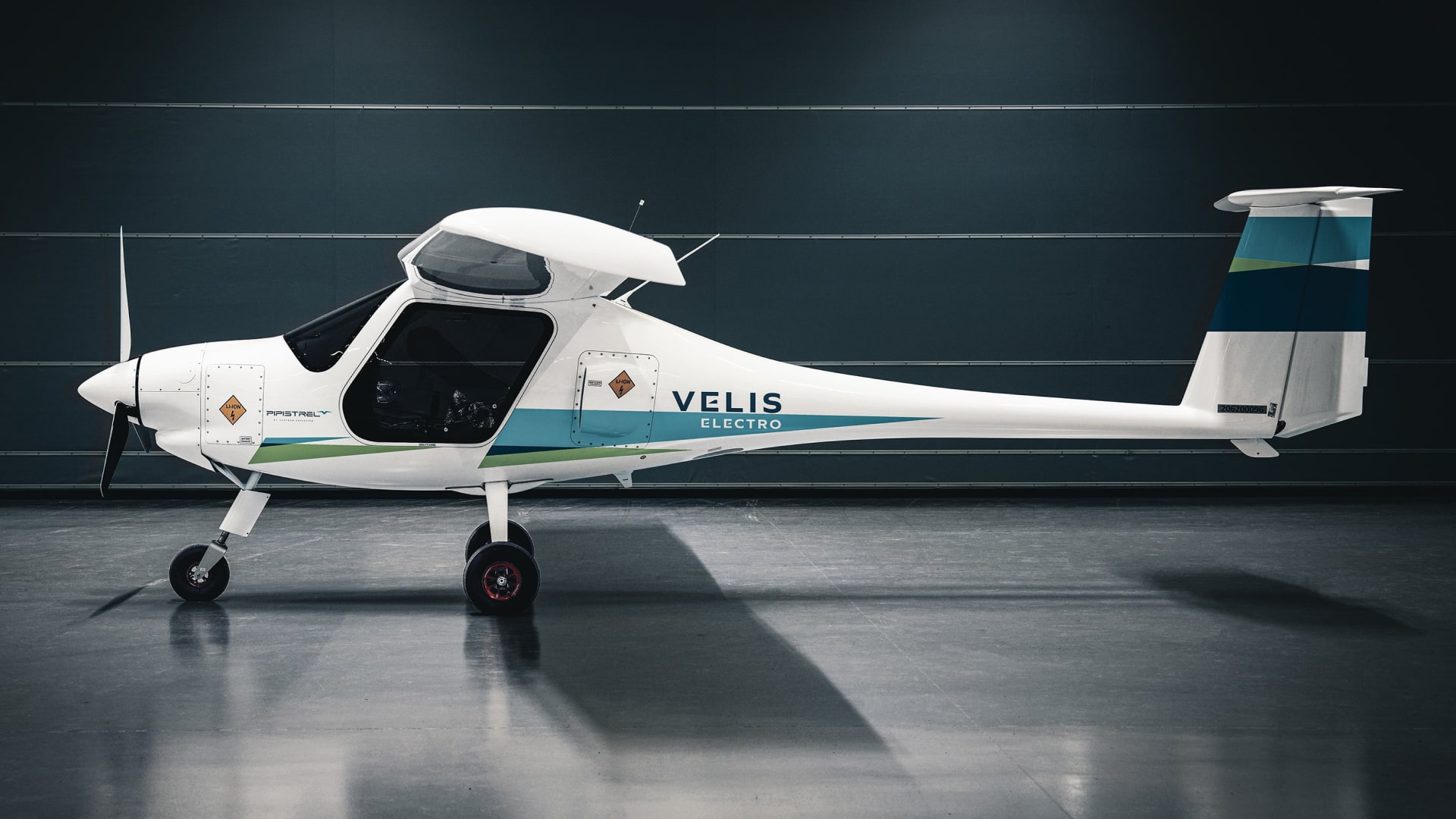
10 June 2020
First Type Certified Aircraft with an Electric Engine
Pipistrel Velis Electro

VIDEOS
Roland Berger
Real Engineering
You want to know more about new technology opportunities?
You want to know more about new technology opportunities?
Check these links below











